- Over 65% of India’s population resides in villages, making rural resilience crucial to the nation’s future.
- Indian villages face multiple challenges, including erratic monsoons, groundwater depletion, agricultural market volatility, and rapid technological changes.
- Despite these challenges, innovative community initiatives like Kerala’s Kudumbashree Movement and Gujarat’s water conservation revolution demonstrate adaptability and innovation.
- Building rural resilience is not just about agricultural sustainability but also about preserving the cultural foundation of the world’s largest democracy.
Key Factors Driving Rural Growth in India
- Infrastructure Development
- Programs like PM Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) and Jal Jeevan Mission enhance rural connectivity and amenities.
- Over 7 lakh kilometers of rural roads have been constructed under PMGSY in 21 years.
- Improved infrastructure boosts market access, supports local enterprises, and reduces regional disparities.
- Digital Inclusion and FinTech Penetration
- Rising smartphone usage and platforms like UPI and AEPS are fostering financial inclusion.
- UPI transactions in rural India grew by 118% in 2023, aided by BharatNet and affordable smartphones.
- Agricultural Reforms and Allied Activities
- Schemes like PM-KISAN and the National Livestock Mission diversify rural incomes through agribusiness, fisheries, and horticulture.
- eNAM enhances farm-to-market efficiency and ensures better pricing for farmers.
- Rise of Rural MSMEs and Start-ups
- Programs like the Startup India Rural Program and MUDRA Yojana support rural entrepreneurship.
- 31% of MSMEs engage in manufacturing, with over 50% located in rural areas.
- Decentralized Renewable Energy Initiatives
- Schemes like PM-KUSUM promote solar energy and clean power solutions, reducing rural energy costs.
- India’s renewable energy capacity grew by 13.5% in 2024, with solar pumps benefiting 2.46 lakh farmers.
- Health and Social Welfare Expansion
- Ayushman Bharat and PMMVY have improved health outcomes and social security.
- Over ₹61,501 crore was spent under Ayushman Bharat for 5 crore hospital admissions by May 2023.
- Rural Tourism and Cultural Heritage
- The Dekho Apna Desh initiative promotes rural tourism, leveraging cultural heritage for revenue generation.
- States like Rajasthan and Kerala have developed eco-tourism circuits, attracting tourists.
- Women Empowerment and SHGs
- SHGs under the National Rural Livelihood Mission have empowered over 8.7 crore women.
- Economic participation has improved family welfare and household incomes.
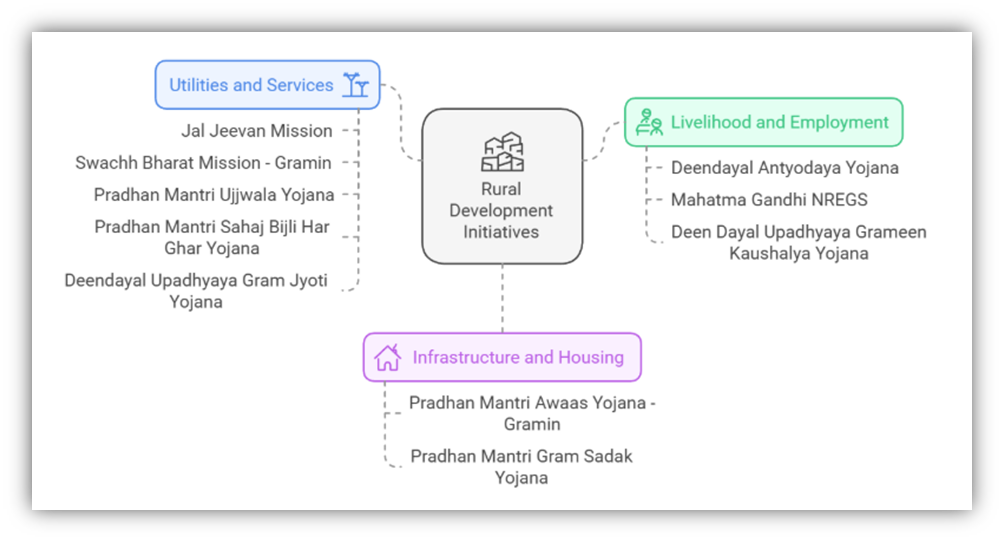
Key Issues Related to India’s Rural Landscape
- Agrarian Distress and Low Income Levels
- Fragmented landholdings, low productivity, and erratic weather impact agriculture.
- Farming households earned an average of ₹13,661 per month in 2021-22.
- Inadequate Health Infrastructure
- Rural areas face shortages in healthcare facilities and trained professionals.
- Only 25% of the rural population has access to modern healthcare locally.
- Educational Inequality and Digital Divide
- Rural schools lack infrastructure, and 43% of children aged 14-18 struggle with English literacy.
- Limited internet access hampers online education.
- Unemployment and Underemployment
- High rural unemployment (9.3% in June 2024) and disguised employment persist.
- Lack of Access to Safe Drinking Water and Sanitation
- While Jal Jeevan Mission has improved water access, challenges like open defecation and groundwater contamination remain.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation
- Climate change exacerbates droughts, floods, and soil degradation, affecting rural livelihoods.
- Social Inequalities and Gender Disparities
- Caste and gender discrimination limit opportunities for marginalized communities.
- Financial Exclusion and Credit Constraints
- Many rural households rely on informal moneylenders despite initiatives like MUDRA Yojana.
- Weak Local Governance and Bureaucratic Inefficiency
- Panchayati Raj Institutions lack the autonomy and resources for effective governance.
- Corruption and inefficiencies undermine rural development programs.
Measures to Promote Rural Growth and Resilience
- Expanding Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA)
- Practices like crop diversification, agroforestry, and solar irrigation can reduce climate vulnerabilities.
- Integrating Technology in Rural Governance
- Platforms like e-Gram Swaraj enhance transparency in fund allocation and monitoring.
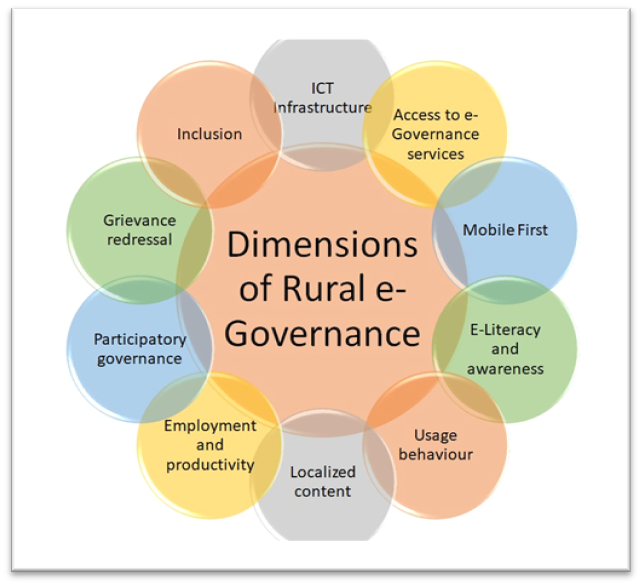
- Strengthening Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
- PPP models can drive skill development, infrastructure, and healthcare projects.
- Promoting Integrated Rural Entrepreneurship
- Linking MUDRA loans with capacity-building initiatives supports diversified rural entrepreneurship.
- Enhancing Local Water Governance
- Projects like Maharashtra’s Jalyukt Shivar Abhiyan have rejuvenated villages through effective water management.
- Mainstreaming Renewable Energy in Rural Development
- Solar micro-grids, biogas plants, and wind energy projects meet rural energy demands sustainably.
- Reforming Agricultural Marketing Systems
- Strengthening eNAM and promoting direct farmer-to-consumer sales can enhance farmer incomes.
- Transforming Rural Transport and Connectivity
- Expanding PMGSY and BharatNet enables better market access and e-commerce integration.
- Developing Sustainable Rural Housing
- Disaster-resilient and eco-friendly housing designs under PM Awas Yojana ensure long-term sustainability.
- Building Grassroots Disaster Management Systems
- Training and early warning systems can prepare rural communities for natural disasters.
- Revitalizing Cooperative Institutions
- Strengthening cooperatives can address credit and marketing gaps in rural areas.
- Fostering Knowledge-Based Agriculture
- Establishing knowledge hubs for farmers can promote modern techniques like hydroponics and organic farming.
- Empowering Youth with Digital and Green Skills
- Training rural youth in green and digital skills can boost employment opportunities.
- Focusing on Inclusive Social Welfare
- Integrating programs like POSHAN Abhiyaan ensures holistic rural welfare.
- Strengthening Rural Healthcare Systems
- Investments in telemedicine and mobile health units improve healthcare access.
- Strengthening Rural Governance
- Empowering PRIs with greater autonomy and resources ensures better scheme implementation.
Conclusion
- Building rural resilience is pivotal for India’s future.
- Holistic approaches integrating infrastructure, technology, and socio-economic empowerment are essential.
- Synergies between government schemes, private-sector participation, and community-driven initiatives hold immense potential for rural development.



