In today’s digital age, e-Governance has become an essential tool for improving the efficiency, transparency, and accessibility of government services. Through the integration of Information and Communication Technology (ICT), e-Governance aims to provide SMART governance, offering citizen-centric services that are simplified, moral, accountable, responsive, and transparent. In this article, we explore the definition, significance, and key initiatives of e-Governance in India.
What is E-Governance?
E-Governance refers to the use of ICT by the government to deliver services, exchange information, and carry out administrative functions. It aims to enhance the interaction between government and citizens, businesses, and other governmental entities, ensuring better governance and improved public service delivery.
SMART Governance
The term SMART Governance highlights the key attributes of e-Governance:
- Simple: Simplifying government rules and regulations through ICT, making processes more user-friendly.
- Moral: The introduction of technology to enhance the efficiency of government processes, leading to better governance.
- Accountable: Effective information management systems to ensure accountability within public services.
- Responsive: Streamlining processes to speed up government functions and respond promptly to public needs.
- Transparent: Making government actions more transparent by sharing information through websites and portals, ensuring public access.
Types of Interactions in E-Governance
E-Governance facilitates four primary types of interactions, each with its own objectives:
- G2C (Government to Citizens)
- This interaction ensures the efficient delivery of public services to citizens. It aims to make government services more accessible and citizen-friendly.
- G2B (Government to Business)
- Facilitates interaction between businesses and the government, aiming to reduce red tape, save time, and improve transparency in business-government dealings.
- G2G (Government to Government)
- Focuses on seamless interaction between various government entities at different levels, boosting efficiency and performance.
- G2E (Government to Employees)
- Ensures efficient communication between the government and its employees, improving administrative efficiency and employee satisfaction.
Advantages of E-Governance
Implementing e-Governance offers several benefits that can significantly improve the functioning of government and its interaction with citizens and businesses:
- Improved Service Delivery: E-Governance enhances the speed and quality of public service delivery.
- Better Business Interactions: It streamlines interactions between businesses and the government, fostering a more transparent business environment.
- Citizen Empowerment: Citizens can access vital information and services, promoting transparency and participation.
- Enhanced Government Management: E-Governance systems increase the efficiency of government operations and management.
- Reduced Corruption: By reducing human intervention and increasing transparency, e-Governance can mitigate corruption.
- Cost Reductions: E-Governance solutions reduce operational costs, saving government resources and boosting revenue.
- Improved Public Relations: It fosters better communication between the government and civil society.
- Flattened Organizational Structure: E-Governance reduces hierarchical layers, making government processes more flexible and efficient.
Key E-Governance Initiatives in India
India has taken several significant steps to promote e-Governance across the country:
- National Task Force on IT and Software Development (1998): This initiative laid the foundation for e-Governance in India.
- Ministry of Information Technology (1999): The creation of this ministry paved the way for implementing ICT initiatives across government departments.
- The Information Technology Act (2000): This act facilitated e-governance by laying down a legal framework for electronic transactions and data protection.
- National e-Governance Plan (NeGP): Launched to improve government service delivery through a set of Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and support components.
- e-Kranti – Electronic Delivery of Services: A major part of the Digital India initiative, e-Kranti focuses on enhancing citizen-centric services and leveraging emerging technologies.
- The National Policy on Information Technology (NPIT) 2012: This policy further boosted the adoption of ICT in government processes.
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP)
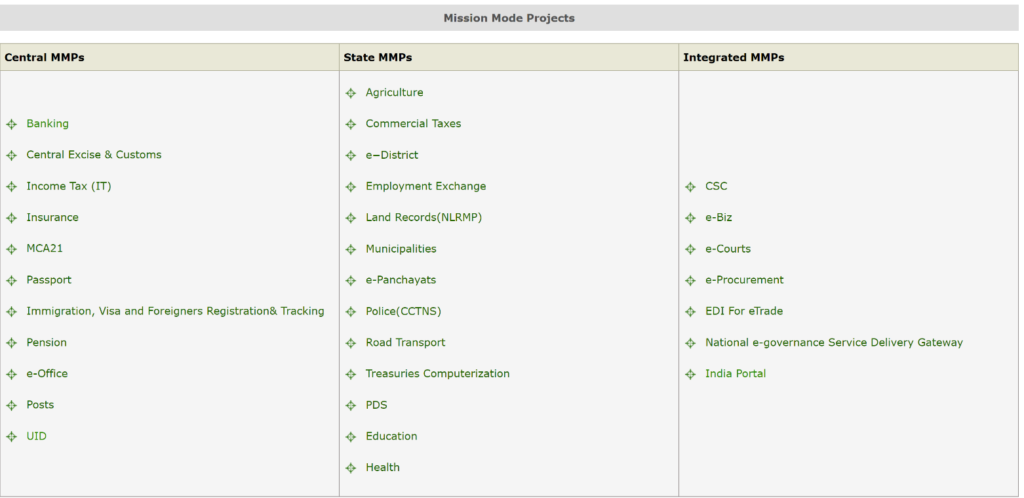
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) aims to provide a comprehensive framework for e-Governance in India. This plan includes a nationwide infrastructure that reaches even the remotest villages, ensuring digitization of records and promoting internet access. NeGP comprises 31 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs), which focus on specific areas of governance, such as land records, banking, and taxation.
e-Kranti: National e-Governance Plan 2.0
e-Kranti is an extension of NeGP under the Digital India Programme. Its objective is to redefine e-Governance by enhancing citizen services and integrating emerging technologies like mobile governance and cloud computing.
Mission Mode Projects (MMP)
A Mission Mode Project (MMP) is an individual initiative within the National e-Governance Plan that focuses on specific areas of governance, such as banking, taxation, and land records. These projects have clear objectives, implementation timelines, and measurable outcomes. There are 31 MMPs classified into central, state, and integrated projects.
National Conference on e-Governance
The National Conference on e-Governance is held annually to discuss e-Governance initiatives and share best practices. The conference, organized by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) and the Department of Information Technology, provides a platform for senior government officials to exchange views on improving e-Governance.
Key Highlights of the 23rd National Conference on e-Governance (2020)
- Theme: “India 2020: Digital Transformation”
- Sub-themes:
- Digital Platforms and Digital Economy
- Building Digital Trust – Transparency, Security, and Privacy
- Digital Payments and Fintech
- Skilling and Capacity Building
- Notable Awards:
- Ayushman Bharat: Gold Award for Government Process Re-engineering.
- Antyodaya Saral Haryana: Gold Award for Citizen-Centric Delivery.
- SAKOON (Jammu & Kashmir): Gold Award for District-Level Initiative.
Conclusion
e-Governance in India is reshaping the way government functions, making it more efficient, transparent, and accessible. Through initiatives like NeGP, e-Kranti, and Mission Mode Projects, the government is working to enhance public service delivery, promote transparency, and empower citizens. The ongoing efforts in e-Governance are helping India transition into a digital governance model that is better equipped to meet the challenges of the 21st century.
By embracing ICT in government services, India is setting an example of how technology can lead to transformational change in governance, improving not just the efficiency of administrative processes but also the overall citizen experience.