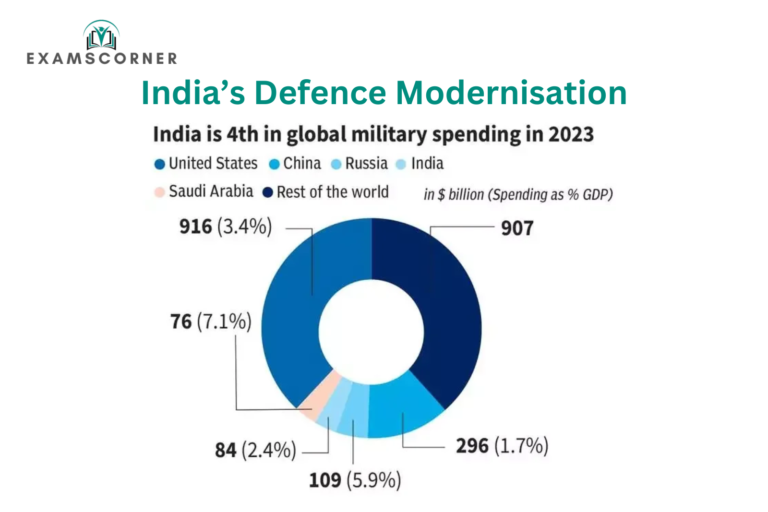
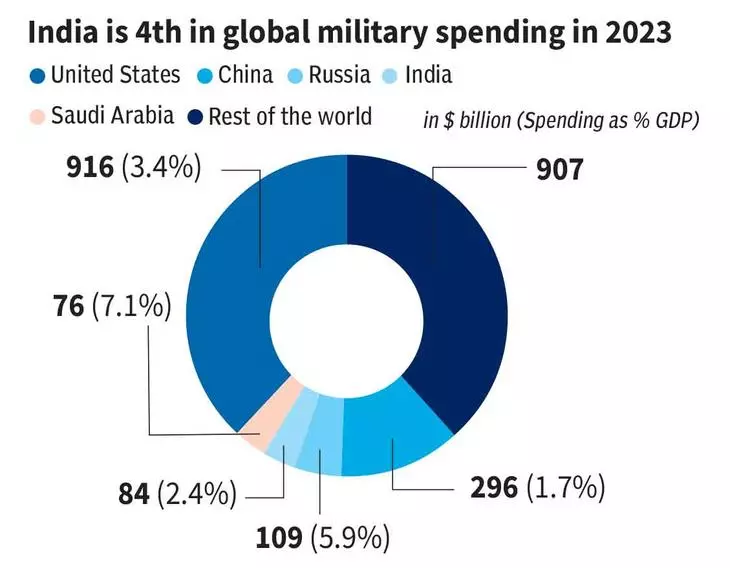
India is the world’s fourth-largest defense spender in 2023, coming after the United States, China, and Russia. India is now focusing on improving its defense capabilities through increased spending on new equipment. Since the pandemic, there has been a big change in the defense sector. The country is importing fewer weapons from other countries and producing more at home. At the same time, India has been exporting more defense equipment, marking an important step toward becoming self-reliant in defense.
Key Developments in India’s Defence Modernisation
Boosting Local Defense Manufacturing
India is working hard to produce more defense equipment locally and reduce its reliance on imports. Policies like the Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020 prioritize buying from Indian manufacturers.
- In 2023-24, India produced defense equipment worth ₹1.27 lakh crore, a 16.7% increase from the previous year.
- About 75% of the defense procurement budget for 2024-25, worth ₹1.40 lakh crore, has been allocated for local products, including advanced weapon systems.
Rise in Defense Exports
India is becoming a strong player in the global defense market by offering cost-effective, high-quality weapons.
- Products like the BrahMos missile and Pinaka rocket systems have received international attention.
- Defense exports reached ₹21,083 crore in 2023-24, a massive increase compared to a decade ago.
- The government aims to increase exports to ₹35,000 crore by 2025 with initiatives like iDEX, which supports the development of competitive technologies.
Partnerships with Global Defense Leaders
India is working with other countries to develop advanced technologies and fill technological gaps.
- Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders and Thyssenkrupp Marine Systems are collaborating on submarines under Project P-75(I).
- India and France have agreed to jointly produce aircraft engines.
- India and the U.S. are co-developing technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and hypersonic systems under the INDUS-X initiative.
Advances in Missile and Tactical Systems
India has made significant progress in developing missiles and other advanced systems.
- The induction of the ‘Pralay’ tactical missile enhances battlefield flexibility.
- Tests of the Agni Prime missile in 2024 improved India’s long-range strike capabilities.
Regional Growth through Defense Corridors
Defense Industrial Corridors in Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh are boosting regional development.
- These corridors aim to attract ₹20,000 crore in investments.
- Tamil Nadu alone has secured commitments worth ₹11,794 crore, with companies like L&T setting up manufacturing units.
Focus on Space and Cybersecurity
India is addressing new-age threats in space and cybersecurity.
- The Defense Space Agency plans to use satellites for surveillance and communication.
- The Gaganyaan mission, scheduled for 2025, may have military applications.
- CERT-In is working on securing defense networks from cyber threats.
Positive Indigenization Lists
India has introduced five Positive Indigenization Lists, banning imports of specific defense items after set deadlines.
- This move has led to innovation, with many components like K9 Vajra artillery systems now produced locally.
- Such steps have significantly reduced dependency on foreign suppliers.
Strengthening Maritime Capabilities
India is building its naval strength to address piracy and protect its interests in the Indo-Pacific region.
- INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, was inducted into the Navy in 2023.
- New patrol vessels are being deployed in areas like the Gulf of Aden to ensure regional security.
Challenges in India’s Defence Sector
Continued Dependency on Imports
India remains one of the biggest arms importers globally, which limits its strategic independence.
- The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war has disrupted the supply of key systems like the S-400 missiles, highlighting vulnerabilities.
Delays in Procurement
India’s process of acquiring defense equipment is slow due to bureaucratic hurdles.
- For example, the Tejas Light Combat Aircraft took decades to develop.
- Submarine projects like Project 75(I) have also faced repeated delays.
Outdated Equipment
A large portion of India’s military equipment is old and needs replacing.
- Tanks like the T-72, used for over 40 years, are still in service.
- Artillery systems like Bofors, inducted in the 1980s, remain in use despite modern alternatives.
Limited Local Manufacturing Capacity
India still depends on foreign technology for critical components like jet engines.
- While defense production increased to ₹1.27 lakh crore in 2023-24, it is not enough to meet global standards.
Budget Constraints
Although the defense budget is increasing, a large portion goes toward salaries and pensions.
- This leaves less money for buying and developing advanced equipment.
Cybersecurity Weaknesses
India’s defense systems face risks from cyberattacks.
- In 2013, Chinese hackers reportedly breached sensitive defense data.
- India lags behind global leaders like the U.S. in cybersecurity preparedness.
Lack of Unified Command
The lack of a joint command structure affects coordination between the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Theater commands, proposed to improve interoperability, are yet to be implemented.
Weak R&D and Skilled Workforce
India spends less than 1% of its defense budget on research and development.
- Projects like the Arjun tank and Kaveri engine have faced delays.
- There is also a shortage of skilled workers in areas like robotics and AI.
Steps to Improve Defense Modernisation
Speeding Up Procurement
- Streamline the acquisition process under DAP 2020 for faster approvals.
- Use AI-driven systems to improve transparency and reduce delays.
Increasing Capital Spending
- Allocate more funds for modernizing equipment like Tejas Mark II aircraft and missile systems.
Strengthening Local Manufacturing
- Link the Make in India and PLI schemes to boost production of critical technologies.
- Support startups and private companies to innovate and manufacture defense equipment.
Enhancing Partnerships
- Collaborate with advanced countries to acquire and develop new technologies.
- Expand initiatives like INDUS-X to include areas like AI and space warfare.
Building Cyber and Space Defense
- Create specialized units for cyber and space security.
- Partner with global leaders to address vulnerabilities.
Implementing Theater Commands
- Integrate the three services under joint theater commands for better coordination.
Supporting Startups and MSMEs
- Expand the iDEX scheme to involve more startups and small businesses in defense innovation.
Strengthening the Navy
- Focus on building new submarines and aircraft carriers to secure the Indo-Pacific region.
Improving Export Policies
- Streamline approval processes and promote products like BrahMos and Akash globally.
Developing Skills and R&D
- Link defense initiatives with Skill India to train workers in advanced manufacturing.
- Increase spending on R&D to develop indigenous technologies.
Conclusion
India’s defense modernization is a journey of balancing self-reliance and global partnerships. Progress in local production, exports, and advanced technology highlights significant achievements. However, consistent efforts in innovation, coordination, and adaptability are key to ensuring long-term security.