Nearly two decades after the devastating 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami, which claimed over 230,000 lives, India has made remarkable progress in disaster management. The enactment of the Disaster Management Act of 2005 established the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), transforming India’s approach from reactive to proactive. Despite these advancements, India’s vast coastline, diverse geography, and increasing climate challenges require ongoing improvements in disaster response and preparedness.
How Has Disaster Management Evolved in India?
Early Years: Relief-Centric and Reactive Approach (Pre-1980s)
- Focus on Relief: In the years following independence, disaster management was focused on immediate relief efforts such as distributing food, providing temporary shelters, and offering medical aid.
- State-Centered Responsibility: State governments took the lead, with central assistance provided during major calamities.
- Challenges: Events like the Bihar famine (1966-67) and Drought of 1972 exposed inefficiencies in relief distribution and the absence of preventive measures.
Shift Toward Planning and Preparedness (1980s-2000s)
- Institutional Focus: The Department of Environment (1980), later the Ministry of Environment and Forests, was created to address disaster-linked environmental concerns.
- Industrial Disasters: The Bhopal Gas Tragedy (1984) highlighted the need for stricter safety regulations and industrial disaster preparedness.
- Cyclones and Earthquakes: Disasters like the Andhra Pradesh Cyclone (1990) and the Latur Earthquake (1993) prompted better relief coordination but lacked prevention and mitigation measures.
- Cyclone Warning System: In 1990, the Cyclone Warning Directorate was established to improve early warning capabilities and provide guidance for cyclone management.
Institutionalization of Disaster Management (2000s)
- Turning Points: The Bhuj Earthquake (2001) and the Indian Ocean Tsunami (2004) exposed vulnerabilities in urban planning and disaster preparedness, pushing for systemic reforms.
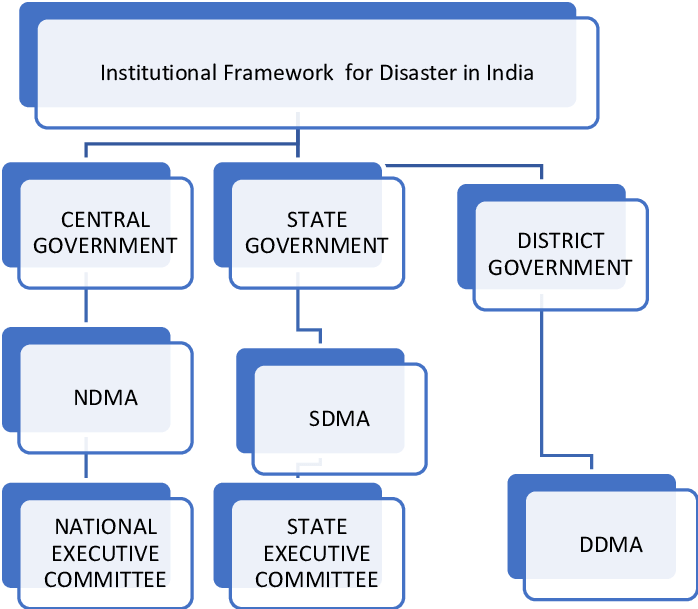
- Disaster Management Act (2005): This Act created a structured framework, establishing the NDMA at the national level and corresponding bodies at state (SDMAs) and district levels (DDMAs).
- Four Pillars of Disaster Management: Focus shifted to mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.
Proactive and Resilience-Focused Approach (2010-Present)
- Risk Reduction: Adoption of global frameworks like the Hyogo Framework (2005-2015) and Sendai Framework (2015-2030) emphasized disaster risk reduction.
- Technology Integration: Use of advanced systems like Doppler Radar and real-time data platforms for better forecasting.
- Community Involvement: Programs like Aapda Mitra and school disaster management plans empower communities as first responders.
- Global Collaborations: India participates in international initiatives like the SAARC Disaster Management Centre and the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Climate Resilience: Focus on nature-based solutions like mangrove restoration under programs like Namami Gange to reduce flooding.
- Urban Resilience: Integration of disaster risk management in urban development under the Smart Cities Mission, with measures like restoring wetlands and improving stormwater infrastructure.
Major Disaster Challenges Facing India
Increasing Climate-Induced Disasters
- Rising Events: India faced extreme weather events on 314 out of 365 days in 2023.
- Cyclone Mocha (2023): Impacted the Sundarbans, while Himachal Pradesh’s record rainfall caused ₹10,000 crore in losses.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Lack of climate-resilient infrastructure worsens the impact.
Urban Flooding
- Rapid Urbanization: Unplanned development has turned cities into flood hotspots.
- Chennai (2021): Outdated drainage systems and wetland encroachments caused severe flooding.
- Bengaluru (2022): Encroachments on lakes and drains led to widespread flooding.
Himalayan Fragility and Glacial Retreat
- Glacier Loss: Between 2000 and 2016, Himalayan glaciers lost 8 billion tonnes of ice annually.
- Disasters: The Kedarnath Flood (2013) and Chamoli Disaster (2021) highlighted risks from hydropower projects and deforestation.
Industrial Hazards
- Lax Safety Norms: Repeated industrial disasters like the Vizag Gas Leak (2020) and Ludhiana Gas Tragedy (2023) show the need for better monitoring and enforcement.
Agricultural Vulnerabilities
- Droughts: Erratic monsoons and groundwater depletion have worsened droughts, as seen in Latur (2022).
- Water Scarcity: By 2030, 40% of Indians may lack drinking water (NITI Aayog).
Forest Fires
- Increasing Fires: The India State of Forest Report (2023) recorded 5,351 forest fires in Uttarakhand alone.
- Impact: The Simlipal Fires (2021) affected a third of the forest area.
Public Health Crises
- Post-Disaster Diseases: Waterborne diseases spiked after the Kerala Floods (2018), exposing gaps in healthcare response.
Weak Early Warning Systems
- Global Ranking: India ranked 14th out of 21 countries in early warning effectiveness, per the World Meteorological Organization (2023).
Gender and Social Inequities
- Vulnerabilities: Women and marginalized groups face heightened risks during disasters, as seen after Cyclone Amphan (2020).
Funding and Institutional Gaps
- Insufficient Funds: Only 20% of the ₹68,463 crore allocated for disaster management (2021-2026) goes to mitigation efforts.
Lessons India Can Learn from Other Countries
- Japan: Strict building codes and earthquake drills.
- Bangladesh: Efficient cyclone evacuation strategies.
- Netherlands: Advanced flood management with dikes and dams.
- South Korea: Integrated digital platforms for disaster response.
- Sweden: Climate adaptation linked to urban planning.
Measures to Enhance Disaster Resilience
Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
- Invest in flood-resistant drainage systems, cyclone-proof housing, and green buildings.
- Replicate Odisha’s cyclone shelters nationwide.
Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction (CBDRR)
- Combine MGNREGA with hazard mapping to build assets like embankments.
Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM)
- Restore wetlands, strengthen river embankments, and integrate Namami Gange with flood prevention plans.
Early Warning Systems
- Use AI, IoT, and satellite monitoring for accurate forecasts.
- Expand the Common Alerting Protocol for local language alerts.
Seismic Safety
- Retrofit buildings in high-risk zones and enforce seismic codes under Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY).
Disaster Insurance
- Expand insurance coverage under schemes like PMFBY for faster payouts.
Urban Resilience
- Mandate risk-sensitive zoning and use startups to develop disaster technologies under Startup India.
Nature-Based Solutions
- Restore mangroves in coastal areas to reduce cyclone impacts and improve carbon storage.
Unified Command Systems
- Establish real-time data analytics centers for efficient coordination.
Gender-Inclusive Policies
- Involve self-help groups (SHGs) in disaster relief and recovery.
Transboundary Cooperation
- Collaborate with neighboring countries through SAARC for shared disaster risks.
Disaster Education
- Incorporate disaster preparedness into school curriculums and expand programs like Aapda Mitra.
Conclusion
India has made significant strides in disaster management since the Disaster Management Act of 2005. However, challenges like climate change, urban flooding, and industrial hazards require a shift from reactive responses to proactive, resilience-focused strategies. With community involvement, technological advancements, and global collaboration, India can build a robust disaster safety net for the future.



