The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) is a flagship agricultural insurance scheme introduced to mitigate risks in farming. By covering crop losses from pre-sowing to post-harvest, it aims to ensure financial security and promote sustainable agricultural practices. Here’s an in-depth look at this comprehensive scheme.
Why in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture launched the National Crop Insurance Portal’s digitized claim settlement module, DigiClaim, under PMFBY. This initiative leverages technology to streamline claim settlements, ensuring faster and transparent compensation to farmers.
Quick Facts
- Purpose: Comprehensive crop insurance from pre-sowing to post-harvest.
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Nature: Demand-driven and voluntary for both States and farmers.
- Beneficiaries: All farmers, including sharecroppers and tenant farmers.
Objectives
- Provide financial support to farmers suffering crop loss/damage.
- Stabilize farmers’ income and encourage credit flow to the agriculture sector.
- Promote the adoption of modern agricultural practices and crop diversification.
Salient Features
- Background:
- PMFBY replaced the National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) and Modified NAIS while retaining the Restructured Weather-Based Crop Insurance Scheme (RWBCIS), which compensates cultivators for deemed crop losses based on weather parameters.
- Crops Covered:
- For Rabi and Kharif seasons: All cereals, millets, pulses, and oilseeds.
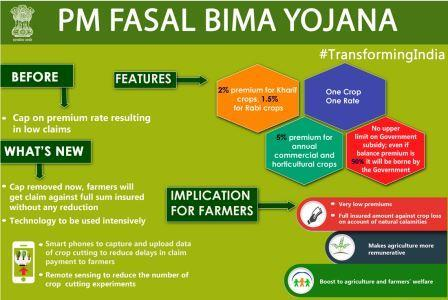
- Premium Structure:
- Premium is calculated as a percentage of the sum assured or the Actuarial Premium Rate (APR) (whichever is less).
- APR is determined by insurance companies.
- Insured Sum for Crops:
- Crops with Minimum Support Price (MSP): States/UTs can opt for the scale of finance or district-level value of notional average yield at MSP.
- Crops without MSP: Farm gate price is considered.
Coverage and Exclusions
- Basic Coverage:
- Mandatory coverage for yield losses (from sowing to harvesting) due to non-preventable risks such as drought, dry spells, floods, and pests.
- Add-On Coverage:
- At the discretion of States, coverage may include risks like prevented sowing, planting, and germination failures.
- Exclusions:
- Losses due to war, nuclear risks, malicious damage, and other preventable causes are excluded.
Operational Provisions
- Area-Based Approach: All farmers within an ‘Insurance Unit (IU)’ face similar risks.
- Aadhaar Mandatory: Ensures unique identification of beneficiaries.
- State Insurance Companies: States can establish their own insurance companies.
- Business Allocation: Insurance companies are selected for three years.
Technological Advancements
To improve efficiency and transparency, several tech-driven initiatives have been introduced:
- DigiClaim:
- Claims processed through the National Crop Insurance Portal (NCIP).
- Payments are directly transferred to farmers’ accounts via the Public Finance Management System (PFMS).
- Farmers can track claim status through SMS alerts and links.
- Weather Information Network Data Systems (WINDS):
- Provides hyper-local weather data for accurate risk assessments.
- Yield Estimation System (YES-TECH):
- Offers precise yield assessment methods at the Gram Panchayat level.
- AIDE/Sahayak App:
- Facilitates door-to-door enrollment to enhance scheme accessibility.
- Geospatial Tools:
- FASAL Project: Forecasts agricultural output using space and meteorological data.
- Bhuvan Geo-Platform (ISRO): Monitors plantation, pest surveillance, and weather conditions.
- NADAMS: Assesses agricultural droughts.
Key Initiatives under PMFBY
- Alternative Risk Models:
- Introduced three models (‘Profit and Loss Sharing’, ‘Cup and Cap (60-130)’, ‘Cup and Cap (80-110)’) to improve efficiency and retain a portion of unused premiums within state treasuries.
- National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGPA):
- Enables timely access to agricultural information using ICT.
Steps Taken to Increase Coverage
- Extended the selection period for insurance companies to three years.
- Introduced innovative risk-sharing models to reduce financial burdens on States.
- Enhanced data collection using real-time observations and photos through the CROPIC platform.
Benefits of PMFBY
- Farmers:
- Reduces financial risks and ensures compensation for crop losses.
- Encourages the adoption of modern agricultural techniques.
- Governments:
- Facilitates improved credit flow to the agricultural sector.
- Promotes economic stability in rural areas.
- Consumers:
- Indirectly benefits consumers by stabilizing food production and supply.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) exemplifies the government’s commitment to building a resilient agricultural sector. By integrating technology and adopting a farmer-centric approach, the scheme ensures timely and transparent compensation, enabling farmers to recover from losses and invest in better practices. With continuous enhancements, PMFBY stands as a robust model for agricultural insurance globally, fostering security and growth in India’s agrarian economy.
For more details or to check your beneficiary status, visit the official PMFBY portal.



